Digital graphic files will generally fall into one of two categories—vector or raster. Vector graphics, such as logo files, use intricate paths made up of points and lines to create an image. Raster graphics, such as digital photographs, are created using a grid of tiny pixels. The purpose of this post is to further explain the difference between these file types and to help determine which type is required for a variety of purposes.
Vector
Vector files, made up of points and lines to create paths, can be scaled up and down without losing quality. This makes vector files the best format for graphic assets such as illustrations, icons and company logos, as the same file can be used for designs ranging from a mobile app to a large billboard without sacrificing quality or increasing file size.

Probably the most common example of vector-based files that we use daily without even realising are font files. Each letter that you type is a vector graphic. You can increase text size or zoom in as much as you want and fonts will still remain clear when viewed online or in standard editable formats such as Word documents.
Although most online graphics are still raster-based, the introduction of vector-based SVG files allows elements like logos, illustrations and icons to be used in apps and web development. This will be an important factor moving forward with responsive site designs, as layouts and design elements are adjusted to fit various screen sizes and resolutions like retina displays.
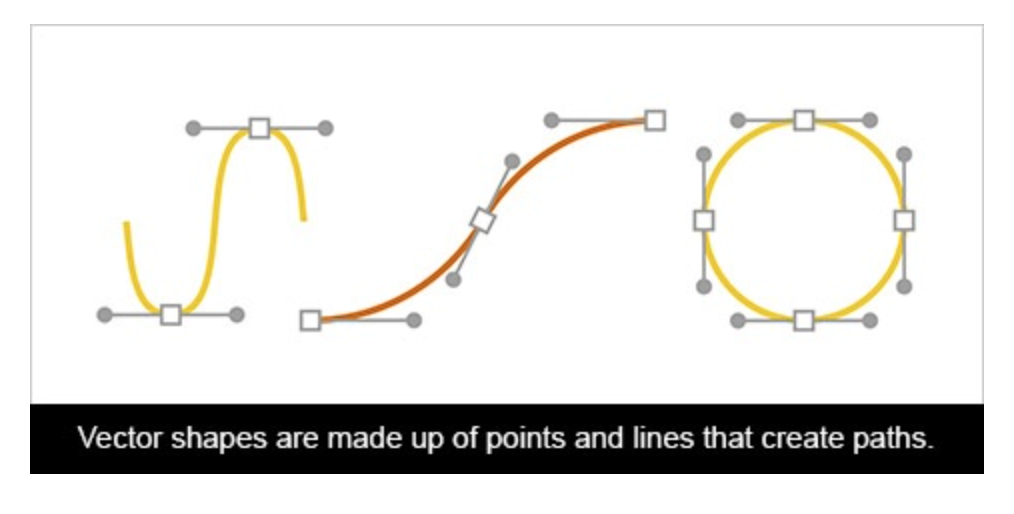
Raster
Raster images are made up of many tiny squares called pixels and are often referred to as ‘bitmap’ images. When zoomed in closely, the individual pixels can be observed. The resolution of a raster file is referred to as DPI (dots per inch) or PPI (points per inch), and is the main determining factor for increasing file size.
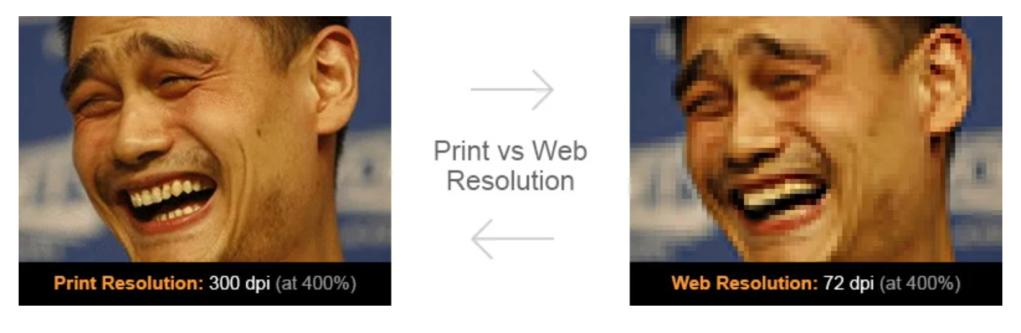
Essentially all digital photography is raster-based. Most graphic files found online are also raster-based and saved for a screen resolution of 72 DPI, a larger file size is usually required for use in printed material where the standard resolution is 300 DPI.
File Extensions
Typically you can distinguish between raster and vector formats by looking closely at the edges of graphic elements like text and logos. File extensions will also suggest which category a file will fall under, though there are always exceptions to the rule.
Raster
.jpg Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG)
.png Portable Network Graphics (PNG)
.gif Graphics Interchange Format (GIF)
.tiff Tagged Image File Format (TIFF)
.psd Adobe Photoshop File
.pat Corel Paint File
Vector
.eps Encapsulated PostScript File (EPS)
.svg Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG)
.ai Adobe Illustrator File
.cdr Corel Draw File
Both
.pdf Portable Document Format (PDF)
Note: Any of the above file types can be exported to a pdf format, so these files can be
either vector or raster or a combination of the two.
Disclaimer: Graphic software has come a long way over the years, resulting in a lot of line-blurring between programs. Raster-based images can be embedded into Adobe Illustrator and vectors can be placed and even created in Photoshop. With this in mind, consult a graphic designer when in doubt. Make sure the designer provides vector logo files when having your logo updated and ask your printer to double-check the resolution of images when having material professionally printed.